When it comes to turnip vs. radish, it is important to know the difference between them. Being similar root vegetables, turnips, and radishes may also look alike, but they still have critical distinctions that set each other apart.
You are not alone because telling between these two vegetables can be challenging. In this post, we will walk you through the differences between turnip and radish so the next time you are at the grocery store, you will be confident in knowing which one to pick.

A turnip is a root vegetable with all edible parts, from the green top to the roots.
Along with cabbage, broccoli, kale, and rutabaga, it belongs to the Brassicaceae family, more commonly known as the mustard or cabbage family.
Turnips taste is mildly earthy, slightly sweet, and somewhat peppery or spicy, especially when eaten raw.
Young, smaller turnips are most commonly eaten, while the bigger, older ones are used to feed livestock such as sheep and cattle.
Like turnips, radishes belong to the mustard family, Brassicaceae.
All the parts of the radish plant are edible as well. They are popular in Asian cuisine and are well-loved for the crunchiness they can add to dishes, primarily when consumed raw.
The radish taste is peppery and slightly spicy. If you prefer a milder flavor, you can try smaller, younger radishes, as they tend to be less spicy.
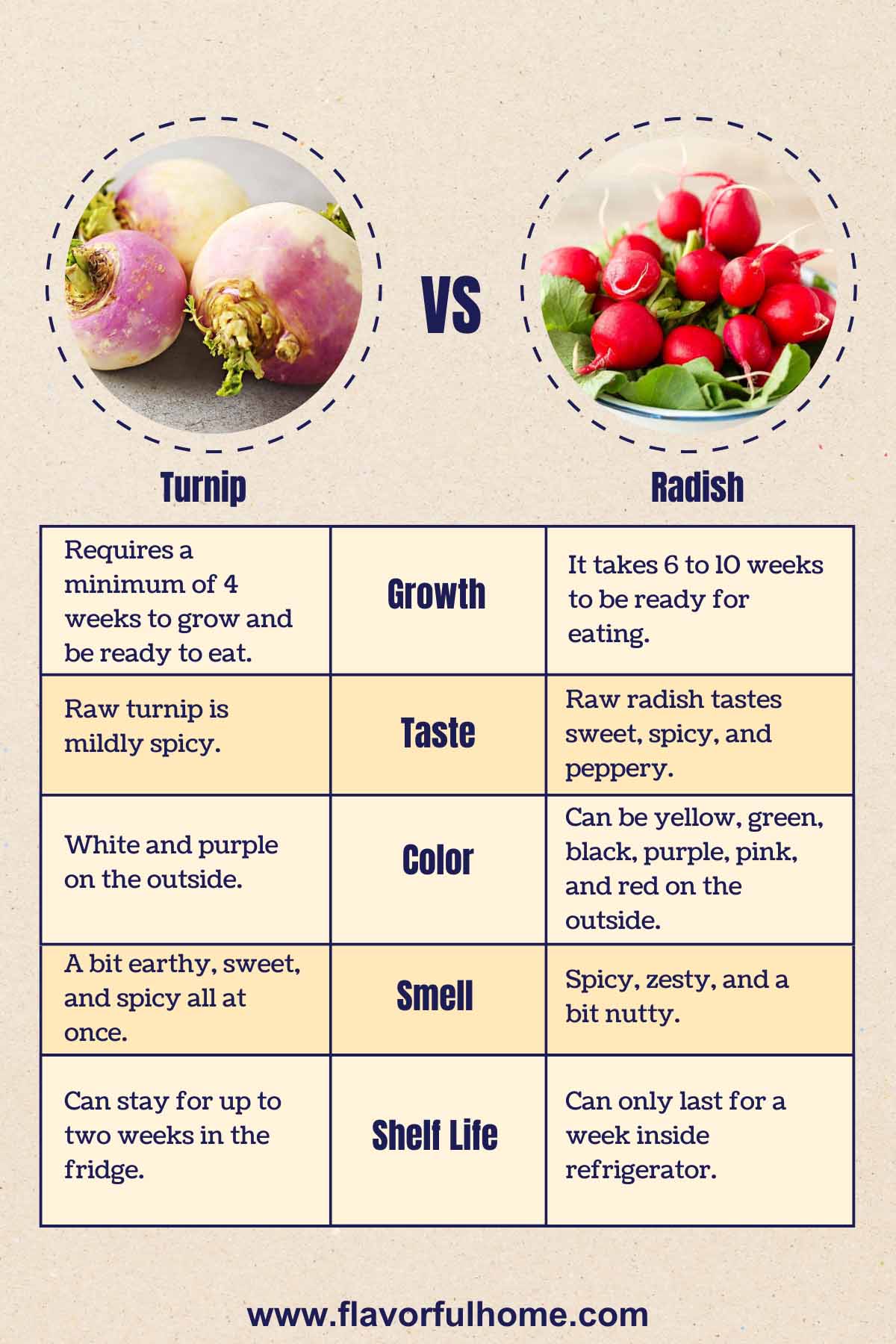
Radishes are one of the easiest plants to grow from seeds because they need fertile, moist soil and abundant sunlight. They germinate quickly but require a minimum of 4 weeks to grow and be ready to eat.
Turnips are easy to grow from seeds, but they take a minimum of 6 weeks to be ready for eating, stretching to up to 10 weeks.
Raw turnips are mildly spicy. However, this taste becomes mellow once cooked, turning earthy and sweet.
Unlike younger turnips, older turnips taste bitter raw but lose the bitterness and become sweet as beets once cooked.
On the other hand, a raw radish tastes sweet, spicy, and peppery. Once cooked, its flavor also mellows and turns much like that of potatoes.
While both radishes and turnips are sweet and spicy, radishes have a more pungent taste than turnips. That being said, if you dislike radishes, you can try turnips for a more subtle flavor.
Radishes also tend to have a mild nuttiness, while turnips lean more on the earthy taste.
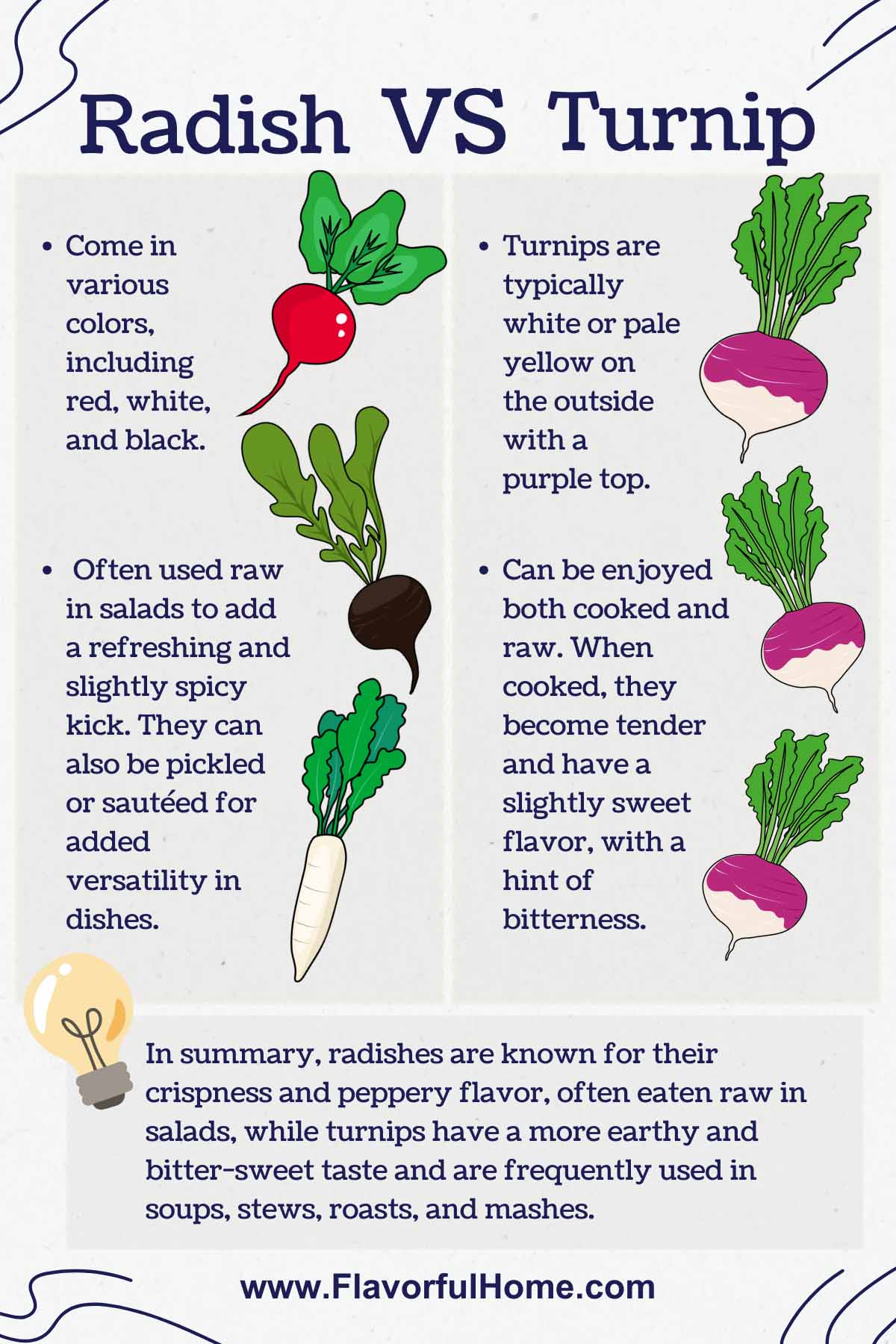
The tap roots, referred to as the turnips themselves, are bulbous. They are usually white and purple on the outside, while their insides are pure white. Sometimes, their exterior can also be a combination of red and white or green and white instead of the usual purple and white.
Due to the many varieties of radishes, their appearances can vary, but the most common radishes can be spherical or cylindrical. Radish can also be yellow, green, black, purple, pink, and red on the outside, but the interior is always pure white.
Turnips and radishes smell just like the taste; turnips smell a bit earthy, sweet, and spicy all at once, while radishes smell spicy, zesty, and a bit nutty.
Radishes, however, have a more pungent scent than turnips.
Both radish and turnip leaves are edible and comparable to mustard greens. However, the leaves of radishes are narrower and more delicate than those of turnips.
In general, turnips last longer than radishes. You can expect turnips stored in a perforated plastic bag in the fridge to stay great for up to two weeks. On the other hand, radishes can only last for a week inside the refrigerator.
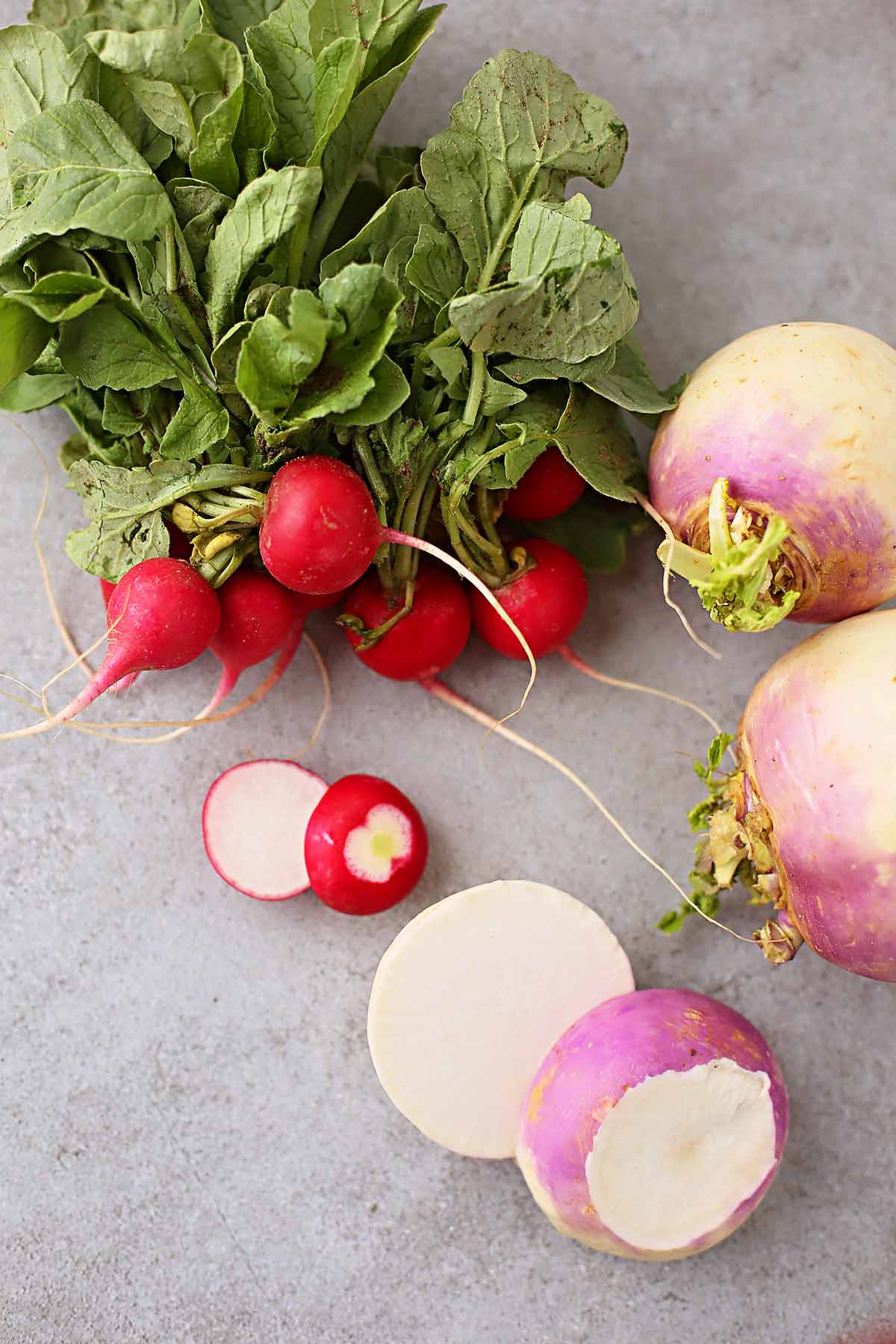

Radishes and turnips share similarities, too, which is why they can be used as substitutes for each other.
The most significant radish vs. turnip similarity is that they are root vegetables within the mustard family. Both can also be eaten raw or cooked, with their greens being edible.
Their insides also look the same, and they are both pure white and crispy when raw. Both radishes and turnips lose their crunch and most of their sharp taste when cooked.
Turnips contain essential nutrients that the body needs to function correctly, such as potassium, which might help improve heart health.
They offer high fiber content. Turnip greens also contain a significant amount of iron that might help improve blood circulation.
Radishes are also good for the heart because they are an excellent source of anthocyanins, which help keep the heart functioning properly, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
They are also high in vitamin C, folic acid, flavonoids, and potassium.
Turnips are an excellent choice if you’re looking for a way to add flavor and nutrition to your stew. You can also use turnips as a side dish for that extra sweetness. Add them to any main dish, and you can enhance the dish’s overall flavor.
Radishes are almost always served raw, and they taste better when paired with lush greens in a salad or eaten with parsley, dill, cilantro, and chives.
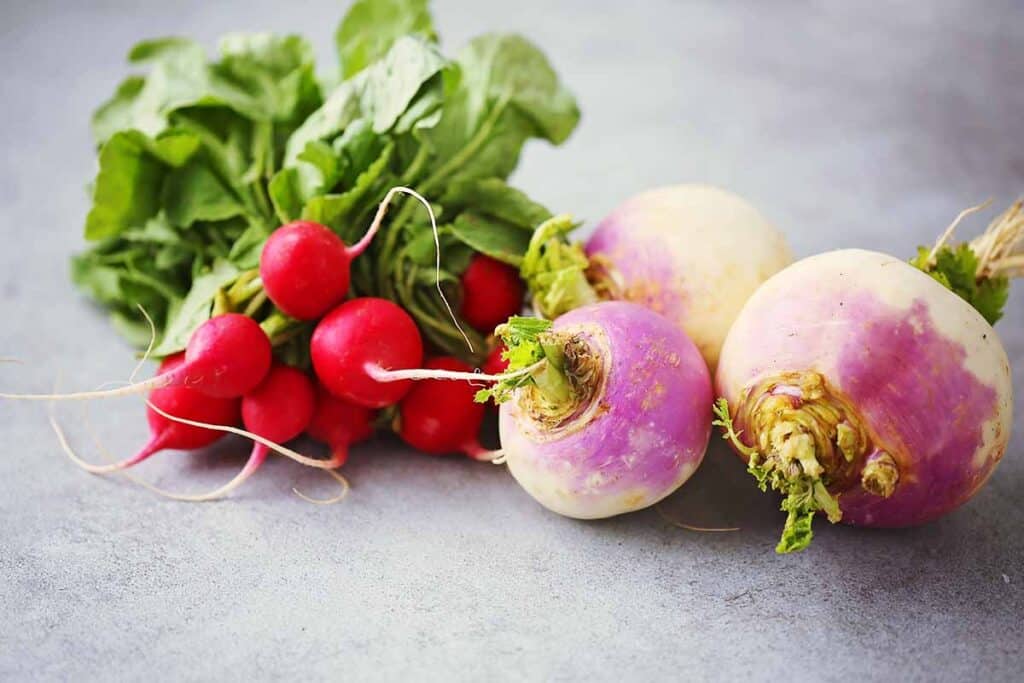

No, turnips and radishes are not the same. They belong to the same plant family but are different vegetables.
Turnips have a milder scent and taste than radishes. Radishes are also usually smaller than turnips. Lastly, turnips take a longer time to grow as compared to radishes.
There is a subtle difference between the taste of turnips and radishes. Both these two root vegetables taste sweet and spicy, but radishes possess a hint of nuttiness and have a more robust flavor than turnips. Turnips, though, have a slightly earthy taste that radishes don’t usually have.
When identifying turnip vs. radish, it is crucial to look past the appearance because they can sometimes look very similar.
Pay attention to other factors such as smell and taste because they will reveal subtle differences that give these two common root vegetable distinctions.
Do not worry, though, if you happen to pick up a radish instead of a turnip in the grocery store because the chances that you can still use it to cook whatever you are making are high – you can use them interchangeably in most recipes.